What Design Thinking is and how it helps companies innovate
An agile and user-centred methodology
Thinking what no one has yet thought and solving problems no one has been able to solve thanks to creative thinking.
Design Thinking methodology enhances companies’ ability to make effective and profitable decisions, leveraging the involvement of various stakeholders, internal and external. It does this by putting teams into a position to develop creative thinking through very cohesive and focused units, where the focus on problems is combined with the identification of potential innovative solutions.
Companies have understood the need to question themselves in order to go beyond working practices that are now obsolete and above all ineffective from a business perspective. They must also develop a culture of continuous development, experimenting and working with those who bring new skills and ideas.
This means learning an open innovation design method that helps in taking a different approach, developing a propensity for action and accepting the possibility of failure because it is precisely from it that we learn most.
What are the advantages of Design Thinking?
One of the main benefits is providing a reliable method for making critical and strategic decisions, drastically reducing the risks associated with them. It also promotes an attitude of listening, collaboration and teamwork, and encourages the possibility of focusing on the needs of people, companies and customers. This methodology improves decision making, creates a culture of innovation, reduces costs and fosters a positive and proactive environment.
What are the fields of application for Design Thinking?
Design Thinking is applicable to all types of problems, concerning strategy, organisation or development of new products and services; it produces the best results for both trivial and complex problems.
Everything starts from people. Behaviour is observed and needs are understood. It is a user-centric method, starting from the consumer/customer, capturing a need or desire and transferring it to the product, and that is how you build a business model that really works.
Who is it aimed at?
Design Thinking is aimed at all those who want to improve their performance, competitiveness and effectiveness. In particular, it is suitable for those companies that want to put innovation at the heart of their strategy and achieve tangible results. Design Thinking can be applied to any type of organisation: from startups to large multinationals to non-profit organisations. It is a method and as such can be successfully applied by both a few and many people, involving different business departments and including active contributions from suppliers, customers, partners, etc.
What is the objective? And what are the principles of Design Thinking?
The objective of Design Thinking is to identify an innovative solution to a problem that satisfies 3 fundamental criteria:
● Desirability: customer centrality, putting ourselves in their shoes.
● Feasibility: identification of themes and models through observation and analysis to assess consumption/purchasing behaviour.
● Profitability or financial sustainability: we must define the winning solution in terms of sustainability and profitability.
This methodology is constructed by placing the user at the centre. Before starting any session it is good to have a clear idea of, and to embrace, the principles of Design Thinking by focusing on the needs of users, the potential of the working team and the spirit of creativity.

FOCUS ON THE CUSTOMER: Design Thinking is born out of the desire to look at the needs of users and help them to achieve them. The role of the end user in the innovation process is crucial. The focus is on listening and understanding their needs. Success at that point is measured on the basis that the customer’s needs are met.
DIVERSIFIED TEAMS: Diversified teams generate many more ideas than a homogeneous team, thus increasing the chances of finding an ad hoc solution. Different skills contribute to the identification of multiple ideas in order to identify the best one focused on the customer’s needs.
CONTINUOUS EXPERIMENTATION: this model is the so-called Loop, a continuous cycle of observation, reflection and implementation. Proceed in whatever order you prefer, undertaking all the necessary iterations. Abstract ideas are given concrete form, exploring continuous possibilities for viable hypotheses that can always be questioned and improved.
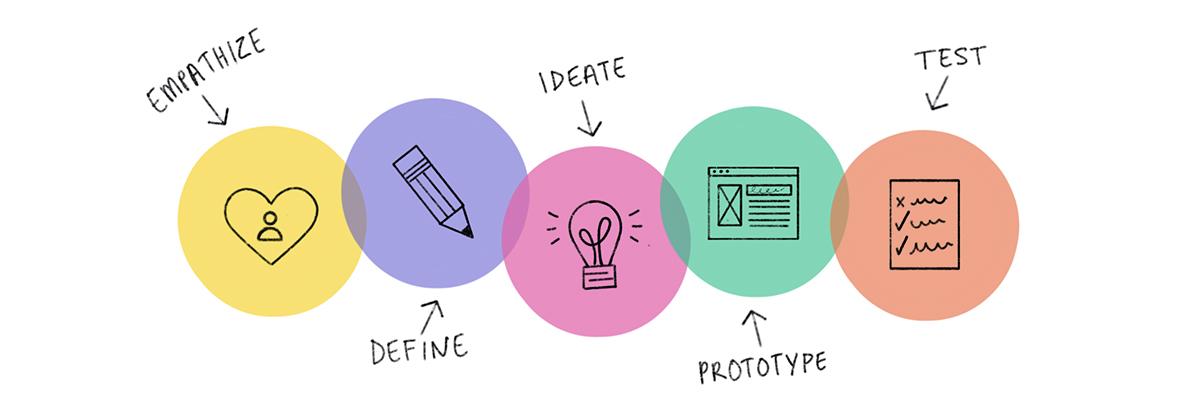
Quali sono le fasi del Design Thinking
1. Empathise: get to know the user and understand their needs, desires and objectives. People are observed and analysed to understand needs and emotional behaviour. At this stage, collect as much real information as possible about the user, setting aside judgements and expectations. This first stage requires attention to detail to define the so-called “personas” that will then be the fulcrum of the entire session, from which ideas and solutions will originate and develop. Getting to know the user is fundamental and neglecting the details could compromise the success of the session.
● Tools: customised searches, direct customer contact.
● Objective: to collect information, stimuli, details in order to bring out opportunities from which to innovate.
2. Define the problem: identify the definition of the user’s problem. It is necessary to define the difficulties and obstacles that users encounter and to delineate the problem that the team is called upon to solve. The problem is analysed by putting yourself in the user’s shoes once the needs have been collected and analysed.
● Tools: personas, customer journey map. Identify the key characteristics of the “personas” by focusing on their buying behaviour based on the context (external factors, needs, values and objectives that influence our persona’s experience), emotional state (note feelings and emotions in the various stages), actions (what the persona wants to do concretely) and key factors (touchpoints and new opportunities).
● Objective: to translate the stimuli received by identifying the basis from which to develop an innovative solution.
3. Ideate: in this phase you have a solid knowledge of the users and a very clear idea of the problem(s). At this point you start designing the solutions. Here you need the creativity and ideation skills of the participants. It is necessary and useful to bring the team together, as often as is useful, in order to collect and compare as many ideas as possible. There are various ideation techniques that you can use such as brainstorming and mind-mapping. Only at the end will the best ideas be identified.
● Tools: ideas generation, mind-mapping, post-its.
● Objective: to develop concepts, potential ideas and solutions, and to define them through continuous testing with users.
4. Prototyping: at this point we move on to the transformation of ideas into tangible products. This is basically a simplified version of the product that incorporates the potential solutions identified in the previous stages. Here any problems and defects emerge and are highlighted and at this point the planned solutions can be confirmed, improved, redesigned or rejected.
● Instruments: Scenarios and Prototyping.
● Objective: to proceed in the definition of strategies, roadmaps and implementation activities.
5. Testing: at this stage you can test solutions on users, which does not mean that this stage represents the end of the process. Feedback from the test may reveal elements for which it will be necessary to redefine the analysis of the original problem or develop new ideas that were not previously thought of.
● Tools: ad hoc according to the business.
● Objectives: to trial solutions by testing them.
What are the results?
The Design Thinking approach allows you to design and develop innovative solutions by fully understanding who the key players are, developing ideas shared by all colleagues and reducing risks by adopting solutions that create value for the customer and the market.
Through this approach companies have the opportunity to expand their competitive reach. Design Thinking today allows you to align the commercial, business and technical needs of Innovation and IT. It therefore provides innovative solutions that meet users’ needs by delivering results quickly and on the appropriate scale.
To find out how Intesa is using Design Thinking to solve user problems and improve customer experiences, contact our team.




